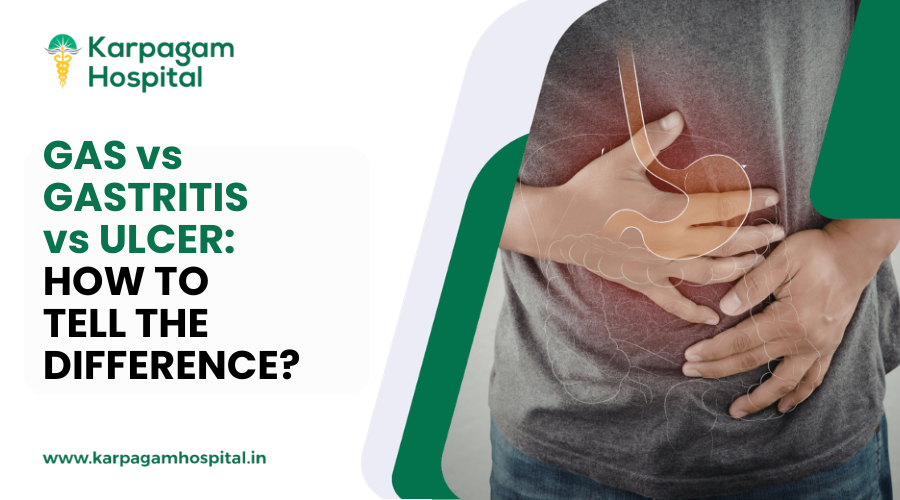
Introduction
Women will need to prioritize their health concerns to maintain their general well-being. Regular screening and appropriate preventive treatment can identify many issues before they become deadly, improving quality of life and outcomes. The article will include the essential tests and preventative strategies from early adulthood to later years.
Regular Women’s Health Screenings
Women’s screenings frequently find health problems early on, even before symptoms or indicators show up. This can lead to better treatment outcomes and a more favorable prognosis. A woman should consider the following vital health exams at different phases of her life.
Breast Cancer Screening
This type of cancer is found predominantly among females. Early detection at times when the disease has spread less can be successfully cured in many cases. There have been recommendations for women to receive routine mammograms when they reach the age of 40. Still, one would be advised to undergo testing earlier if there is any family history or increased chance for the disease.
Cervical Cancer Screening
Another cause of great concern is cervical cancer for women, especially sexually active women above 30 years of age. Pap smears, referred to as Pap tests, are the usual tests for cervical cancer. Such tests check the precancerous cells before they become cancerous. Recommendations from the American Cancer Society should begin at age 21 and maintain it every three years until reaching age 65. Screening is also subject to an individual’s risk factors.
Heart Disease and Blood Pressure Monitoring
Heart disease is the leading cause of death for women. It’s crucial to monitor heart health through regular blood pressure checks and cholesterol tests. Starting at age 20, women should get their blood pressure checked regularly. This is especially important if there’s a family history of heart attack disease or other risk factors such as diabetes, smoking, or obesity.
Bone Density Testing
Women are at higher risk of osteoporosis as they age, particularly after menopause. Osteoporosis causes bones to become weak and brittle, increasing the likelihood of fractures. A bone density test, typically recommended at age 65, can help identify the condition early, allowing for intervention before severe bone loss occurs.
Skin Cancer Screening
Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer in the U.S as well as women are not immune to its risks. Annual skin checks by a dermatologist are an important part of preventive care. In addition to professional screenings, women should also practice regular self-exams, looking for new moles or any changes in existing ones, which could signal skin cancer.
Colon Cancer Screening
Colon cancer is often diagnosed in the later stages, but routine screenings can help catch it early. The American Cancer Society recommends that women begin screening for colorectal cancer at age 45. Options for screening include colonoscopies, stool tests, and flexible sigmoidoscopy, among others.
The Value of Preventive Healthcare for Women
Preventive care is the key to a woman’s security over her lifetime. Preventing illnesses includes routine examinations, screenings, immunizations, and lifestyle modification. When preventive care is incorporated into standard medical treatment, the chances for major illnesses, including osteoporosis, heart disease, and breast cancer, are reduced.
If they are detected early, many disorders that afflict women, such as autoimmune diseases or cervical cancer, can be effectively controlled.
Regular Exercise and Healthy Diet
A balanced lifestyle is one of the significant preventive care considerations. Regular exercise improves cardiovascular fitness, controls weight, helps reduce stress, and has a lowered risk of developing chronic diseases. The CDC recommends that adults engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity weekly. Equally important in the health system are a woman’s diet requirements for foodstuff.
Her diet should provide fruits, vegetables, proteins, and fats. Intake should be low processed and low on sodium and sugars, with less risk of high blood pressure or diabetes and lesser risks of obesity and any serious complications leading from these dangerous diseases.
Vaccinations
Vaccines are of great importance in preventing infectious diseases. Women should be up-to-date on recommended vaccines, such as the flu shot, HPV vaccine to prevent cervical cancer, and the Tdap vaccine to protect against tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis. Women aged 50 or older should discuss shingles and pneumonia vaccines with their providers.
Mental Health Support
Mental health is included in the general concept of well-being, yet one often forgets that maintaining it is an integral component of preventive care. Mindfulness, meditation, or talking to a therapist can help women overcome everyday pressure. As a result, checkup emotional health prevents issues ranging from depression to anxiety issues.
Smoking Cessation and Alcohol Moderation
Smoking is an increased risk factor for numerous illnesses, including lung cancer, heart disease, and stroke. Any lady who smokes must, therefore, try her best to stop smoking for her well-being. Women who use alcohol should take alcohol moderately because this can be detrimental if not limited. The CDC requires only one drink in a day for women, as increased levels of drinking will bring other illnesses like liver diseases and heart diseases.
Women’s Health at All Life Stages
Women’s health needs change with age, and various life stages require different care and screenings.
Women in Their 20s and 30s
In young adulthood, the primary focus should be on forming healthy habits. A woman should regularly exercise, eat well, and maintain an ideal weight, among other good habits. She also needs to establish contact with a primary care provider for routine health checks, including pap smears and breast exams. Women in their 30s begin discussing family planning and their reproductive health.
Women in Their 40’s and 50’s
As women reach their 40s, the need for regular screenings becomes even more pressing. Mammograms and cholesterol tests become increasingly important, and women should discuss menopausal symptoms and hormone replacement therapy options with their doctor. Bone density testing should also be considered as women approach menopause.
Women Over 60
Women above 60 should continue undergoing regular screening tests and focus more on bone health, cardiac risks, and being active. This is also the best time to attend to most postmenopausal health problems, including osteoporosis and cognitive decline risks. Finally, maintaining mental and emotional well-being is very important at this stage.
Common Health Issues in Women and Ways to Prevent Them
Women at different life stages face specific health challenges, many of which are preventable with the proper preventive measures.
Breast Cancer
While breast cancer cannot be entirely prevented, a healthy lifestyle coupled with regular breast screenings can reduce the risk. Therefore, women should always take care to know their history and any changes in their breasts. Early detection is the key to good treatment.
Heart Disease
According to earlier statements, heart disease is the leading cause of death among women. The diet must contain heart-healthy foods. Regular exercise and monitoring blood pressure and cholesterol levels are fundamental requirements to reduce the risks of heart disease.
Diabetes
Women are more likely to be affected by type 2 diabetes, especially if they have a family history of the disease or have excessive body weight. Eating well, exercising regularly, and monitoring blood glucose helps in preventing or controlling this disease.
Conclusion
Women’s health is complex. With the proper screenings, preventive care, and lifestyle choices, they can minimize risks for potentially serious health problems and live much longer and healthier lives. Informed and proactive on screenings, maintaining healthy habits, and addressing health issues at all stages of life, women can optimize health and well-being. Investing in a future full of vigor and good health is a matter of preventive care.
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this blog post is intended for general informational purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this blog.